1. Introduction
In this next series of posts on memorizing the processes, we move on to the final step 6, which is memorizing the INPUTS & OUTPUTS associated with each of the 42 processes. In order to breakdown the memorization into more bite-size chunks, I am going to break down this topic into at least 9 posts, one for each knowledge area. (There may be some knowledge areas that require more than one post.)
This post covers chapter 11 of the PMBOK® Guide, which covers the Risk Management Knowledge Area. This knowledge area contains 6 processes, five of which is in the Planning Process group, and the last of which is in the Monitoring & Controlling Process Group.

2. Review of processes in Risk Management Knowledge Area
As a review, here is a chart which gives a summary of the processes themselves, plus the tools & techniques used as part of that process.
| Process Number & Name |
Process Description | Tools & Techniques |
| 11.1 Plan Risk Management | Defining how to conduct risk management activities for a project.
|
1. Planning meetings and analysis |
| 11.2 Identify Risks | Determining which risks may affect the project objectives and documenting their characteristics. | 1. Documentation reviews 2. Information gathering interviews. 3. Checklist analysis 4. Assumptions analysis 5. Diagramming techniques 6. SWOT analysis 7. Expert judgment
|
| 11.3 Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis | Prioritizing risks for further analysis by assessing likelihood & impact. | 1. Risk probability and impact assessment 2. Probability and impact matrix 3. Risk data quality assessment 4. Risk categorization 5. Risk urgency assessment 6. Expert judgment
|
| 11.4 Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis | Numerically analyzing the effect of risks on project objectives. | 1. Data gathering and representation techniques 2. Quantitative risk analysis and modeling techniques 3. Expert judgment
|
| 11.5 Plan Risk Responses | Developing options and actions to enhance opportunities and reduce risk. | 1. Strategies for negative risks or threats 2. Strategies for positive risks or opportunities 3. Contingent response strategies 4. Expert judgment
|
| 11.6 Monitor and Control Risks | Tracking identified risks, implementing risk response plans if risks occur, and evaluating risk process effectiveness. | 1. Risk reassessment 2. Risk audits 3. Variance and trend analysis 4. Technical performance measurement 5. Reserve analysis 6. Status meetings |
3. Definition of inputs, outputs
The inputs for a given process are the documents or results of other processes that are used in order to do the process. The results of going through the process are the outputs. These outputs are then used as inputs for some other process.
4. Generic inputs
Before we start, there are two “generic” inputs that are used in many, many processes. The term “generic” inputs is not to be found in the PMBOK® guide; that’s just my term I made up in our study group to clue people in to the fact that they are included as an input in more processes than you could probably name off the top of your head.
A. ENVIRONMENTAL ENTERPRISE FACTORS (EEF)
This is the “company culture”, or factors that are external to the project but which influence the project’s success. These can include the company databases and, in particular, the project management software used by the company.
B. OPERATIONAL PROCESS ASSETS (OPA)
Written procedures, policies, and guidelines that are used by the company to guide all operations, including projects. Lessons learned would be an important part of OPA.
Think of the operational process assets as the “hard copy” (written procedures), and the environmental enterprise factors as the “soft copy” (software and the company culture or “unwritten rules” that govern how work is done).
NOTE: Tools & Techniques will be listed for the purpose of completeness and for reference, but their detailed description will be omitted, because it is contained in the blog posts specifically covering Tools & Techniques for that knowledge area.
11.1 PLAN RISK MANAGEMENT
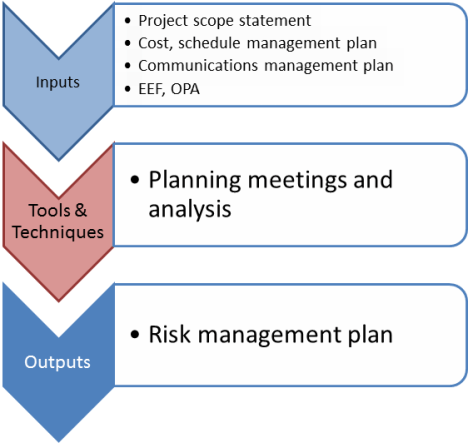
To remember the inputs for this process, remember that the purpose of this process is to define how to conduct risk management activities for a project.
INPUTS
11.1.1 Project scope statement
The project scope statement is the output of the 5.2 Define Scope process.
11.1.2 Cost management plan
The cost management plan defines how risk budgets, contingencies, and management reserves will be reported and assessed.
11.1.3 Schedule management plan
The schedule management plan defines how schedule contingencies will be reported and assessed.
11.1.4 Communications management plan
The communications management plan defines how information on various risks will be shared.
11.1.5 Enterprise environmental factors
The attitudes and tolerances towards risk are part of a company culture.
11.1.6 Organizational process assets
Risk categories, standard templates for statements of risks
TOOLS & TECHNIQUES (for details, see Tools & Techniques Risk post)
11.1.1 Planning meetings and analysis
OUTPUTS
11.1.1 Risk management plan
This includes the following elements (RM stands for risk management in the following table):
| Component | Explanation (answers what question?) | |
| 1. | Methodology | How will RM be performed? |
| 2. | Roles and responsibilities | Who will handle and lead RM activities? |
| 3. | Budgeting | What funds are needed for RM? |
| 4. | Timing | How often will RM be performed |
| 5. | Risk categories | How are risks categorized according to their source (technical, external, organizational, or PM-related)? |
| 6. | Risk probability & impact definitions | What does /low/moderate/high risk mean in terms of impacts on project? |
| 7. | Probability & impact matrix | What are probabilities of risk occurring and what it its impact on project? |
| 8. | Stakeholders’ tolerances | What are tolerances for risk among various stakeholders? |
| 9. | Reporting formats | How are the results of RM processes to be communicated to stakeholders? |
| 10. | Tracking | How will risk events be tracked for the purpose of the project and for inclusion in lessons learned for future projects? |
11.2 IDENTIFY RISKS
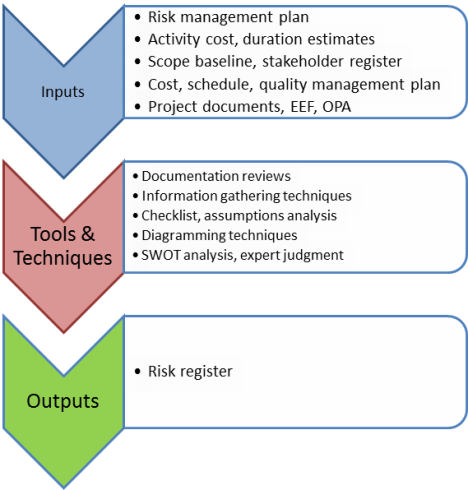
To remember the inputs for this process, remember that the purpose of this process is to determine which risks may affect the project.
INPUTS
11.2.1 Risk management plan
This is the output for the process 11.1 Plan Risk Management.
11.2.2 Activity cost estimates
This is the output for the process 7.1 Estimate Costs.
11.2.3 Activity duration estimates
This is the output for the process 6.4 Estimate Activity Durations.
11.2.4 Scope baseline
This is the output for the process 5.3 Create WBS.
11.2.5 Stakeholder register
This is the output of the process 10.1 Identify Stakeholder.
11.2.6 Cost management plan
This is part of the project management plan, which is the output of the process 4.2 Project Management Plan.
11.2.7 Schedule management plan
This is part of the project management plan, which is the output of the process 4.2 Project Management Plan.
11.2.8 Quality management plan
This is part of the project management plan, which is the output of the process 4.2 Project Management Plan.
11.2.9 Project documents
Assumptions log, network diagrams, and other information valuable in identifying risks.
11.2.10 Enterprise environmental factors
Published information (industry studies, academic studies, etc.) useful for identifying risks.
11.2.11 Organizational process assets
Risk statement templates, and lessons learned from previous projects.
TOOLS & TECHNIQUES (see Tools & Techniques Risk post for details)
11.2.1 Documentation reviews
11.2.2 Information gathering techniques
11.2.3 Checklist analysis
11.2.4 Assumptions analysis
11.2.5 Diagramming techniques
11.2.6 SWOT analysis
11.2.7 Expert judgment
OUTPUTS
11.2.1 Risk register
The risk register identifies each risk, indicates what impact it would have on the project if the risk were to occur, and identifies potential responses to that risk.
11.3 PERFORM QUALITATIVE RISK ANALYSIS

To remember the inputs for this process, remember that the purpose of this process is to take the risks that have been identified in the previous process and to prioritize them by estimating their probability of occurrence and impact.
INPUTS
11.3.1 Risk register
This is the output from process 11.2 Identify Risks.
11.3.2 Risk management plan
This is the output from process 11.1 Plan Risk Management.
11.3.3 Project scope statement
This is the output from the process 5.2 Scope Statement.
11.3.4 Organizational process assets
Information about risks from previous projects.
TOOLS & TECHNIQUES (see Tools & Techniques Risk post for details)
11.3.1 Risk probability and impact assessment
11.3.2 Probability and impact matrix
11.3.3 Risk data quality assessment
11.3.4 Risk categorization
11.3.5 Risk urgency assessment
11.3.6 Expert judgment
OUTPUTS
11.3.1 Risk register updates
The risk register, which is an output of the 11.2 Identify Risk process, is updated with the following categories of information: risk categories, risk priority, risk causes, risk responses, watchlists (low-priority risks), and list of risks needing more analysis.
11.4 PERFORM QUANTITATIVE RISK ANALYSIS

To remember the inputs for this process, remember that the purpose of this process is to take the risk events that have been identified in the 11.2 Identify Risks process, and prioritized in the 11.3 Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis process, and to analyze what the effect of these will be on the project objectives.
INPUTS
11.4.1 Risk register
This is the output from the 11.2 Identify Risks process.
11.4.2 Risk management plan
This is the output from the 11.1 Plan Risk Management process.
11.4.3 Cost management plan
This is part of the project management plan, which is the output of the process 4.2 Project Management Plan.
11.4.4 Schedule management plan
This is part of the project management plan, which is the output of the process 4.2 Project Management Plan.
11.4.5 Organizational process assets
Information about risks from previous projects.
TOOLS & TECHNIQUES
11.4.1 Data gathering and representation techniques
11.4.2 Quantitative risk analysis and modeling techniques
11.4.3 Expert judgment
OUTPUTS
11.4.1 Risk register updates
The risk register is an output of the 11.2 Identify Risks process, and is updated as part of the 11.3 Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis process. It is further updated as part of this process by additional of the following categories of information: probabilistic analysis of the project, probability of achieving cost and time objectives, prioritized list of quantified risks, and trends in quantitative risk analysis results.
11.5 PLAN RISK RESPONSES

To remember the inputs for this process, remember that the purpose of this process is to enhance opportunities and reduce threats to project objectives.
INPUTS
11.5.1 Risk register
This is an output of the process 11.1 Identify Risks.
11.5.2 Risk management plan
This is an output of the process 11.2 Plan Risk Management.
TOOLS & TECHNIQUES
11.5.1 Strategies for negative risks or threats
11.5.2 Strategies for positive risks or opportunities
11.5.3 Contingent response strategies
11.5.4 Expert judgment
OUTPUTS
11.5.1 Risk register updates
To the risk register that is an output of the processes 11.2 Identify Risks, 11.3 Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis, and 11.4 Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis, the list of risks according to priority are updated with strategies for risk responses for when they occur.
11.5.2 Risk-related contract decisions
There are risks related to the fulfillment of contracts. Contracts are one form of mitigating or transferring risk.
11.5.3 Project management plan updates
Any of the components of the project management plan may be updated as a result of the development of risk responses.
11.5.4 Project document updates
Assumptions logs.
11.6 MONITOR AND CONTROL RISKS
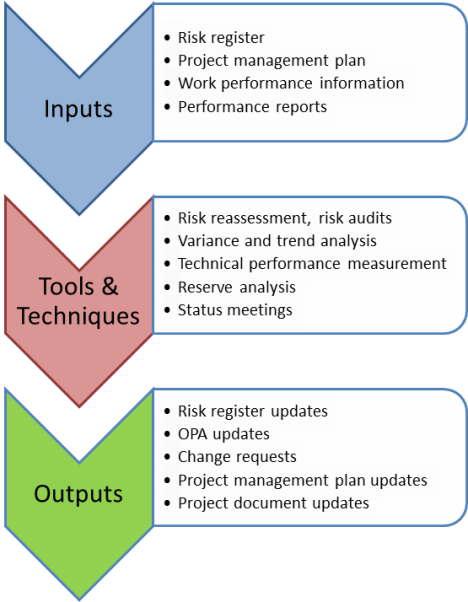
To remember the inputs for this process, remember that the purpose of this process is the process of implementing risk responses plans, monitoring risks, identifying new risks, and evaluating the effectiveness of the overall risk management process.
INPUTS
11.6.1 Risk register
This is the output of the previous four processes 11.2 through 11.6 (updated throughout each process).
11.6.2 Project management plan
This is the output of the 4.2 Develop Project Management Plan.
11.6.3 Work performance information
This is the output of the process 4.3 Direct and Manage Project Execution
11.6.4 Performance reports
This is the output of the process 10.5 Report Performance.
TOOLS & TECHNIQUES
11.6.1 Risk reassessment
11.6.2 Risk audits
11.6.3 Variance and trend analysis
11.6.4 Technical performance measurement
11.6.5 Reserve analysis
11.6.6 Status meetings
OUTPUTS
11.6.1 Risk register updates
To the risk register that is an output of the previous 4 processes, details of risk audits, periodic risk reviews, and risk reassessments are added.
11.6.2 Organizational process assets updates
Lessons learned for future projects.
11.6.3 Change requests
If risks occur which require contingency plans or workarounds as part of a risk response, these may require a change request.
11.6.4 Project management plan updates
Risk management plans may need to be updated.
11.6.5 Project document updates
Assumptions logs updates may need to be updated for the purpose of future projects.
The next post will cover the inputs and outputs of the Procurements Knowledge Area.
Filed under: Uncategorized |


Thanks for the definition of inputs, outputs, it really help me today.
You’re welcome. Once you understand what the process actually DOES, then the inputs and outputs start to make more sense…